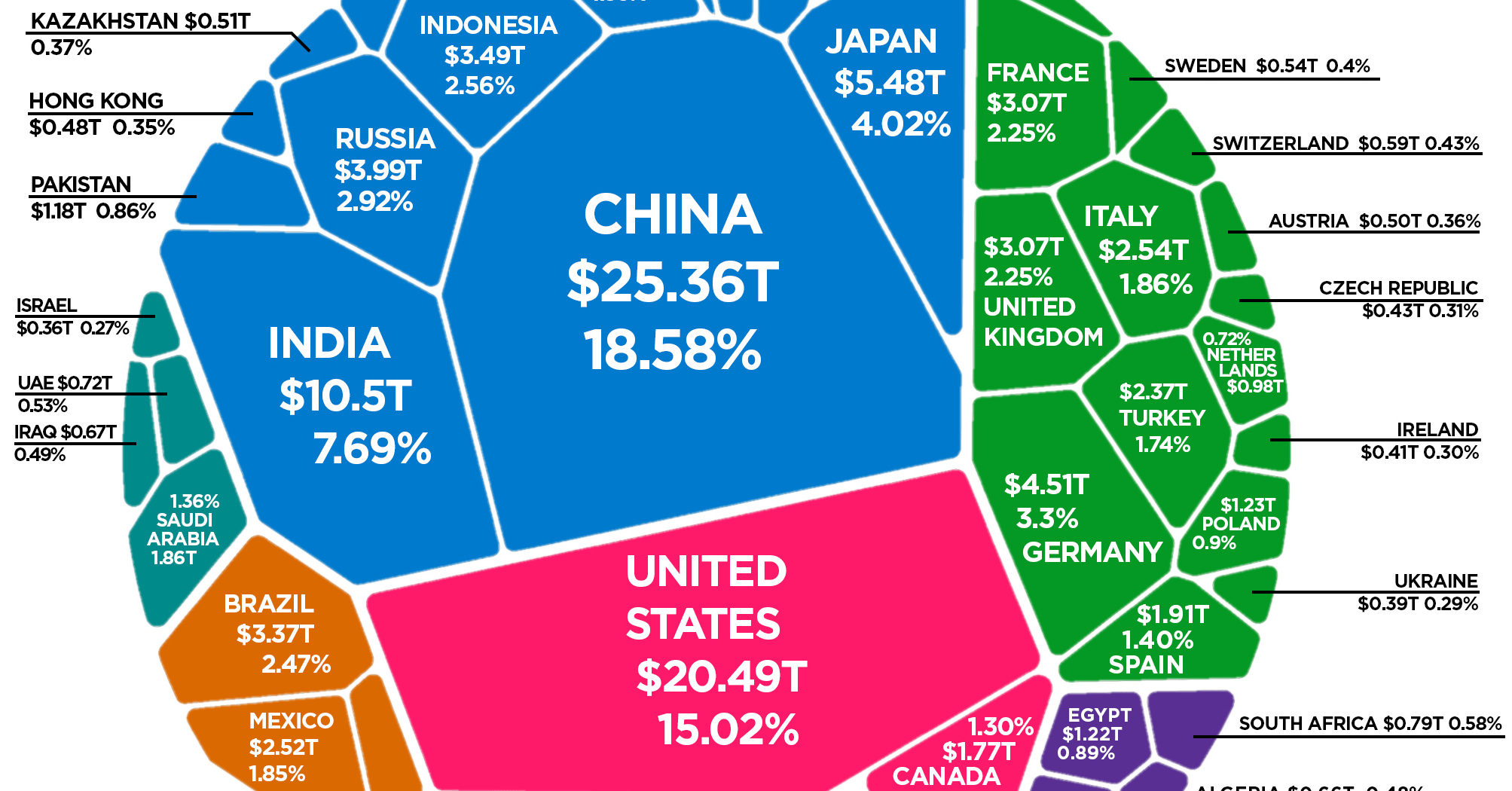
Gross Domestic Product (GDP) is one of the most critical economic indicators used to measure the health and growth of an economy. It plays a pivotal role in shaping economic policies and provides valuable insights into a country's economic performance. As a foundational concept in macroeconomics, GDP helps policymakers, investors, and businesses make informed decisions. But what exactly is GDP, and why does it matter so much? This article will explore these questions and more.
As economies evolve and become increasingly interconnected, understanding GDP becomes essential for anyone interested in global economic trends. Whether you're a student, an economist, or a business owner, knowing how GDP works and its implications can significantly enhance your ability to navigate the complexities of modern economics.
This guide will delve into the definition, calculation methods, significance, and limitations of GDP, along with its impact on economic policy and global markets. By the end of this article, you'll have a comprehensive understanding of GDP and its relevance in today's world.
Read also:Alana Cho The Rising Star In The Fashion And Entertainment Industry
Table of Contents
- What is GDP?
- Types of GDP
- How to Calculate GDP
- Importance of GDP
- Limitations of GDP
- GDP and Economic Growth
- GDP Per Capita
- GDP and the Global Economy
- Historical Perspective of GDP
- Conclusion
What is GDP?
GDP, or Gross Domestic Product, refers to the total monetary value of all goods and services produced within a country's borders over a specific period, typically a year or a quarter. It serves as a key indicator of a nation's economic health and is used to compare the economic performance of different countries. GDP encompasses all sectors of the economy, including agriculture, manufacturing, services, and more.
There are three main approaches to calculating GDP: the expenditure approach, the income approach, and the production approach. Each method provides a unique perspective on the economy's performance, and they should theoretically yield the same result.
Why is GDP Important?
GDP is crucial because it offers a snapshot of a country's economic activity and growth. Policymakers rely on GDP data to make informed decisions about fiscal and monetary policies. Investors use GDP figures to assess the potential risks and opportunities in various markets, while businesses use it to evaluate market trends and consumer demand.
Types of GDP
GDP comes in several forms, each serving a specific purpose:
- Nominal GDP: Represents the value of goods and services at current market prices without adjusting for inflation.
- Real GDP: Adjusts nominal GDP for inflation, providing a more accurate measure of economic growth.
- GDP Growth Rate: Measures the percentage change in GDP from one period to another, indicating the pace of economic expansion.
- GDP Per Capita: Divides GDP by the population to determine the average economic output per person.
How to Calculate GDP
The calculation of GDP involves summing up all the expenditures, incomes, or production values within an economy. The most common method, the expenditure approach, uses the following formula:
GDP = C + I + G + (X - M)
Read also:Jenna Lamia The Rising Star In The Entertainment Industry
- C: Consumer Spending
- I: Investment
- G: Government Expenditures
- X: Exports
- M: Imports
Steps to Calculate GDP
To calculate GDP effectively, follow these steps:
- Gather data on consumer spending, investment, government expenditures, exports, and imports.
- Plug the values into the formula mentioned above.
- Adjust for inflation to obtain real GDP if necessary.
Importance of GDP
GDP is vital for several reasons:
- Economic Indicator: It provides a clear picture of a country's economic health and growth.
- Policy Tool: Governments use GDP data to formulate economic policies and budgets.
- Investment Guide: Investors rely on GDP to evaluate market opportunities and risks.
- Global Comparison: GDP allows for comparisons between countries, helping to identify economic leaders and laggards.
Limitations of GDP
Despite its importance, GDP has several limitations:
- Excludes Non-Market Activities: GDP does not account for unpaid work, such as household chores or volunteer work.
- Ignores Income Distribution: GDP does not reflect how income is distributed among the population.
- Does Not Measure Quality of Life: GDP does not consider factors like environmental sustainability, education, or healthcare quality.
Alternatives to GDP
Some economists propose alternative measures to complement GDP, such as:
- HDI (Human Development Index): Combines health, education, and living standards.
- GPI (Genuine Progress Indicator): Incorporates social and environmental factors.
GDP and Economic Growth
Economic growth is often measured by changes in GDP over time. A positive GDP growth rate indicates an expanding economy, while a negative rate suggests a contraction. However, sustained GDP growth requires balancing various factors, including inflation, unemployment, and productivity.
Factors Affecting GDP Growth
Several factors influence GDP growth:
- Consumer Spending: Higher consumer demand can boost GDP.
- Investment: Increased business investment can drive economic expansion.
- Government Policies: Fiscal and monetary policies play a crucial role in shaping GDP growth.
GDP Per Capita
GDP per capita is a measure of a country's economic output per person. It provides insights into the standard of living and economic well-being of a nation's citizens. However, GDP per capita does not account for income inequality or non-monetary factors affecting quality of life.
How to Calculate GDP Per Capita
To calculate GDP per capita, divide a country's GDP by its population:
GDP Per Capita = GDP / Population
GDP and the Global Economy
In today's interconnected world, GDP plays a significant role in shaping the global economy. Countries with higher GDP often have more influence on international trade, finance, and politics. However, global economic challenges, such as climate change and inequality, require collaborative efforts beyond GDP measurements.
Impact of Global Events on GDP
Major global events, such as pandemics or financial crises, can significantly impact GDP. For instance, the 2008 financial crisis led to a decline in GDP worldwide, while the COVID-19 pandemic caused unprecedented disruptions in global economies.
Historical Perspective of GDP
The concept of GDP was developed during the Great Depression as a tool to measure economic activity and guide recovery efforts. Since then, it has evolved into a cornerstone of economic analysis, with refinements and adaptations to reflect changing economic realities.
Evolution of GDP Measurement
Over the years, economists have introduced new methods and metrics to enhance GDP's accuracy and relevance. These include adjustments for inflation, the inclusion of digital economies, and the incorporation of environmental factors.
Conclusion
GDP remains one of the most important tools for understanding and analyzing economic performance. While it has limitations, its ability to provide a broad overview of economic activity makes it indispensable for policymakers, investors, and businesses. By considering GDP alongside other indicators, we can gain a more comprehensive understanding of economic health and growth.
We invite you to share your thoughts and insights on GDP in the comments below. Additionally, explore other articles on our site to deepen your knowledge of economics and global trends. Together, we can foster a better understanding of the world's economic landscape.
/gdp-increase-636251500-c69345ee97ba4db99375723519a2c1bd.jpg)